Explain the differences between parallel running and direct changeover as ways of implementing the new system.
Direct changeover – new system replaces existing system immediately/overnight
Parallel running – new system runs alongside/together with existing system
Parallel running – there is always the old system to fall back on in the event of the new system failing/information is not lost/always a second copy
Direct changeover – if things go wrong lose all data/old system is not available
Direct changeover – training is more difficult to organise
Parallel running – training can be gradual Parallel running is more expensive to implement than direct changeover....
Direct changeover is a quicker method of implementation than parallel running
Direct Changeover: The old system is stopped completely, and the new system is started. All of the data that used to be input into the old system, now goes into the new one.
Parallel Running: The new system is started, but the old system is kept running in parallel (side-by-side) for a while. All of the data that is input into the old system, is also input into the new one. Eventually, the old system will be stopped, but only when the new system has been proven to work.

What situations are likely to call for the use of Direct Changed Over?

State a stage in system development where each of the following activities are carried out (KCSE 2018)
(a) Identifying technologies that may be used in a proposed system
(b) Identifying the shortcomings of the old system
(c) Prepares the software migration plan

Describe the problem recognition and definition stage of system development

There are four change-over methods used in the implementation stage of the system development life cycle (SDLC): direct change-over, phased, parallel and pilot.
Direct Change-Over
Phased

The introduction of a new system involves evaluation and maintenance once the system is
implemented.
Describe the evaluation and maintenance stage of the systems development life cycle (SDLC)
and provide one example of an activity undertaken in this stage.

A company has decided to deliver its products online to international customers. It has employed you as a project manager to determine whether this is a viable business decision. You choose to conduct a feasibility study. Outline the purpose of a feasibility study using two components associated with this process.

Describe one task that is commonly undertaken during the first phase of system development life cycle

Outline one advantage and one disadvantage of interviews and questionnaires as data gathering techniques.
Interviews
Advantages
Disadvantages
Questionnaire
Advantages
Disadvantages

Describe the purpose of a data dictionary, using an address book database as an example.

Give two characteristics of each of the system development methodologies listed below.
(a) Linear/Cascade/Waterfall
(b) Iterative Methodology
(a) Linear/Cascade/Waterfall
(b) Iterative Methodology

At which stage of the system development life cycle does the changeover to a new system take place?

What characterises a phased implementation approach?
- Phased means that only one part of the system is implemented at a time

Give one reason why a phased implementation would be the best approach to follow in this case.

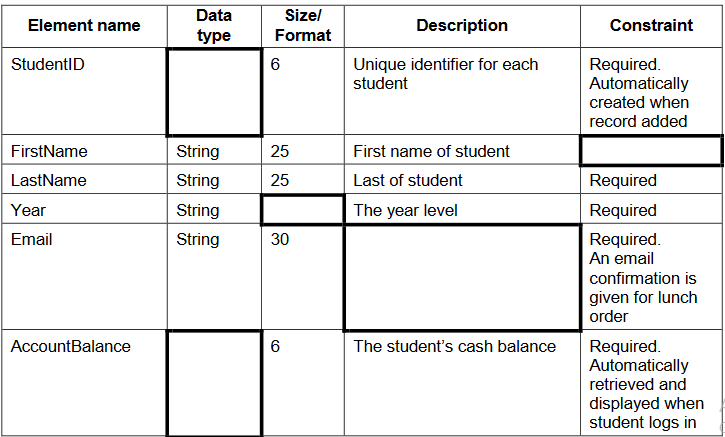
Complete the data dictionary below for the Student entity.
State four tasks performed at the analysis stage in systems analysis.

State advantages and disadvantages of the following system implementation strategies
Phased:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Pilot:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Direct:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Parallel:
Advantages:

State the contents of a feasibility study report

Explain why the organization's management and the analyst need to work together to define the problem accurately during system development

A company has decided to use a computer for stock control. Describe the process of systems development from the time the decision was made to proceed with computerisation until final testing.
specify output requirements
design documents/screen displays
data for input/storage
form design
storage devices
file structures/access/design
data security/back up files
systems flowchart etc.
implementation i.e. pilot/intermediate/parallel running
testing strategy
training
hardware/software
programming/algorithms
validation
user manual
technical documentation
entering data into system

State the reasons for system review and maintenance

Name three of the stages in the system life cycle
– fact finding
– feasibility study
– analysis
– design
– testing
– documentation
– implementation/changeover/installation
– evaluation
– maintenance
